testicular torsion test kryptoco|cremasteric reflex testicular torsion : exporter exporters exporting Prehn's sign is a clinical finding that helps clinicians determine whether testicular pain is caused by epididymitis or testicular torsion. A positive Prehn's sign, characterized by pain relief from the maneuver, is indicative of . webThe f95, f2003, f2008, and f2018 values specify strict conformance to the Fortran 95, Fortran 2003, Fortran 2008 and Fortran 2018 standards, respectively; errors are given for all extensions beyond the relevant language standard, and warnings are given for the Fortran 77 features that are permitted but obsolescent in later standards.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da MCBBS
Prehn's sign is a clinical finding that helps clinicians determine whether testicular pain is caused by epididymitis or testicular torsion. A positive Prehn's sign, characterized by pain relief from the maneuver, is indicative of .Testicular Workup for Ischemia and Suspected Torsion (TWIST) diagnoses testicular torsion, decreasing indication for ultrasound. Testicular torsion is a clinical diagnosis, and patients typically present with severe acute unilateral scrotal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Physical examination may reveal a high-riding.
Testicular torsion is a surgical emergency that is managed with either septopexy-only or tunica vaginalis flap with septopexy if the testis is potentially viable or orchiectomy if .
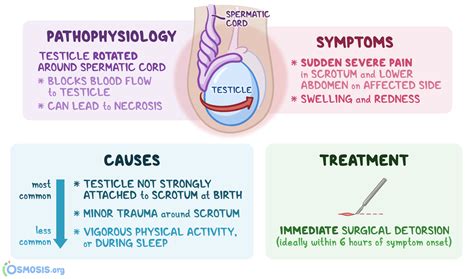
Testicular torsion (TT) occurs when the testis twists along the spermatic cord, compromising blood supply. 1 It is a urological emergency that requires prompt intervention. Testicular torsion is a true urologic emergency, and early identification is critical to prevent the need for testicular amputation. Ultrasound is the ideal imaging modality to evaluate .
Testicular torsion is a fertility-threatening surgical emergency. Case. A 61-year-old male comes to the emergency department complaining of gradual onset of worsening right scrotal swelling. He first noticed the swelling .
Testicular torsion is an emergency condition due to rotation of the testis and consequent strangulation of its blood supply. Symptoms are acute scrotal pain and swelling, nausea, and vomiting. Diagnosis is based on physical .Individual clinical findings that best predict testicular torsion include nausea and vomiting, past trauma, a tender testicle, an abnormal testicular lie (i.e., elevated or transverse), and an. Testicular torsion is a urologic emergency caused by the twisting of the testicle on the spermatic cord leading to constriction of the vascular supply, time-sensitive ischemia, .
Prehn's sign is a clinical finding that helps clinicians determine whether testicular pain is caused by epididymitis or testicular torsion. A positive Prehn's sign, characterized by pain relief from the maneuver, is indicative of . What Is Testicular Torsion? Testicular torsion is when a your testicle twists around. (The word torsion means “to twist.”) The motion also twists the spermatic cord that connects to the testicle.↑ Blaivas, M, et al. Emergency evaluation of patients presenting with acute scrotum using bedside ultrasonography. Academic Emergency Medicine. 2001; 8(1):90-93. ↑ Barbosa, JA, et al. Development of initial validation of a scoring system to diagnose testicular torsion in children. The Journal of Urology. 2013; 189:1853-8. ↑ Gordon J, Rifenburg RP. . Spermatic Cord .
Testicular torsion is a twisting of the spermatic cord and its contents and is a surgical emergency affecting 3.8 per 100,000 males younger than 18 years annually. It accounts for 10% to 15% ofTesticular torsion is when the spermatic cord above your testicle twists, cutting off blood flow to your testicle. Testicular torsion can happen at any age, but it most often happens to boys ages 12 to 18 or babies. Without blood supply, the tissue of your testicle can die in a few hours . See a doctor right away if you think you have . Introduction. Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord and its contents twists within the tunica vaginalis, compromising the blood supply to the testicle.. Testicular torsion is a surgical emergency, as without treatment the affected testicle will infarct within hours.Whilst theoretically it can occur at any age, peak incidence is in neonates and .
Testicular torsion in young boys and teen boys occurs when the testicles are not completely attached in the scrotum. This lets the testicles move more freely and twist. . He may also have tests, such as an ultrasound. This is a painless imaging test that uses sound waves to see the scrotum and testicles and check blood flow. Testicular torsion refers to the torsion of the spermatic cord structures and subsequent loss of the blood supply to the ipsilateral testicle. . Menon VS, et al. Transscrotal Near Infrared Spectroscopy as a Diagnostic Test for Testis Torsion in Pediatric Acute Scrotum: A Prospective Comparison to Gold Standard Diagnostic Test Study. J Urol .
Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord becomes twisted. This causes a restriction in blood flow to the testes, severe pain, and possibly permanent damage. Find out what causes this . How common is testicular torsion? Testicular torsion occurs in teenage boys aged 13-18 years. This is found to happen in around 1 in 4,000 young men. Newborn babies and younger children sometimes develop this problem. It is uncommon over the age of 25 but does occur sometimes in older adults and can occur at any age.Testicular torsion is the twisting of a testis on its spermatic cord so that the blood supply to the testis is blocked. Testicular torsion causes sudden, severe pain and later swelling of the affected testis. A doctor's examination and sometimes ultrasonography are needed for testicular torsion diagnosis. Treatment is to untwist the spermatic cord.The recommendations on management of testicular torsion are based on the European Association of Urology (EAU) guideline Paediatric urology [Radmayr, 2021], the Royal College of Surgeons (RCS) joint publications Asymptomatic scrotal swelling, commissioning guide [] and Management of paediatric torsion, commissioning guide [], and expert opinion in review .
On physical exam, the scrotum is blue and firm with some erythema. Transillumination test is negative. Doppler ultrasound shows absent blood flow. The neonate is immediately sent to hospital for surgery. Introduction. . Testicular Torsion Renal - Testicular Torsion; Listen Now 15:31 min. 9/6/2021. 48 plays. 0.0 (0)Testicular torsion is the twisting of a testis on its spermatic cord so that the blood supply to the testis is blocked. Testicular torsion causes sudden, severe pain and later swelling of the affected testis. A doctor's examination and sometimes ultrasonography are needed for testicular torsion diagnosis. Treatment is to untwist the spermatic cord. Testicular torsion is a very serious condition and is considered a medical emergency. Rotation of the testicle around the spermatic cord can cause obstruction of the arterial blood flow to the testicle, as well as the venous .
Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord (from which the testicle is suspended) twists, cutting off the blood supply to the testicle. [3] The most common symptom in children is sudden, severe testicular pain. [1] The testicle may be higher than usual in the scrotum and vomiting may occur. [1] [2] In newborns, pain is often absent and instead the scrotum may become .If you are a male who experiences sudden and severe pain in your belly, groin or testicle, Bruce Schlomer, M.D., Pediatric Urologist at Children's Health℠ and Associate Professor at UT Southwestern, has an important message for you: "Don't try to tough it out!" These may be signs of testicular torsion – a relatively common medical condition that requires immediate .Testicular torsion can occur at any time – e.g. while sleeping, sitting on the couch, or after activity and trauma. Rapid growth of the testicles during puberty is also a risk factor. Who is at risk of testicular torsion? Most cases are between the ages of 12 and 18, but testicular torsion can occur at any age. Signs and symptoms
Each year, testicular torsion affects one in 4,000 males younger than 25 years. Early diagnosis and definitive management are the keys to avoid testicular loss. All prepubertal and young adult . Testicular torsion is characterized by sudden-onset unilateral testicular pain, which may radiate to the lower abdomen, with nausea and vomiting. Clinical findings include a high-riding. testis. with an absent . cremasteric reflex. Imaging with .
Testicular torsion is a surgical emergency that is managed with either septopexy-only or tunica vaginalis flap with septopexy if the testis is potentially viable or orchiectomy if not. Minimizing time from ischemia onset to surgery maximizes the likelihood of testicular preservation. While factors such as time from door to OR can be easily targeted, others such .Testicular torsion is the twisting of a testis on its spermatic cord so that the blood supply to the testis is blocked. Testicular torsion causes sudden, severe pain and later swelling of the affected testis. A doctor's examination and sometimes ultrasonography are needed for testicular torsion diagnosis. Treatment is to untwist the spermatic cord. Testicular torsion is a urologic emergency caused by the twisting of the testicle on the spermatic cord leading to constriction of the vascular supply, time-sensitive ischemia, and/or necrosis of testicular tissue. Laher A, Ragavan S, Mehta P, et al. Testicular torsion in the emergency room: A review of detection and management strategies.How is testicular torsion diagnosed? Diagnosis entails a physical examination and a complete medical history. A prompt diagnosis is imperative because prolonged testicular torsion may cause irreversible damage to the testes. Other diagnostic tests may be done, but there is no test that diagnoses testicular torsion accurately all the time.
Testicular torsion can occur at any age but commonly occurs soon after birth or between the ages of 12–18 years with a peak in incidence at age 13–14 years. . With regards to the intraoperative bleeding test, all patients with grade 3 bleeding (major bleeding that requires multiple hemoclips and sessions of hemocoagulation) required .B. Ultrasound evaluation with Doppler color flow Testicular torsion should be suspected in patients who complain of acute scrotal pain and swelling. Testicular viability is in jeopardy with delay in diagnosis, ultimately impacting the patient fertility.
testicular torsion treatment
testicular torsion surgery guidelines
testicular torsion physical therapy
Ujizz dot triple X, the website where you are going to have a good time watching HD porn and sex movies, and where all the hottest babes love to try new things. See amateur babes and porn stars at the same time on our hot porn tube. There is no similar website to this one, with Free Porn that you can be sure of - enjoy and click to watch top adult movies!
testicular torsion test kryptoco|cremasteric reflex testicular torsion